There was a time when women were just the kitchen keepers and the house keepers in the society. But now woman has come out of those four walls of the house to rub shoulder with the men. Today’s woman is maintaining a right balance in between work and home. Apart from rearing children, cooking meals and doing household chores, she is pursuing her career as well. Women are socialized to be the caretakers of others. In this fast paced life, they try to juggle every responsibility and pay least attention to their own health. They often spend less time nurturing their own emotional and physical needs. In this scenario, we need to encourage every women to take charge of their health. Here, I am writing on 5 most common health problems of women which are of great concern to them.
OSTEOPOROSIS
Osteoporosis which means “porous bone” is a progressive disease that thins and weakens your bones, making them fragile and more likely to break. It develops gradually over many years without causing any symptoms. Being female, puts you at greater risk of developing osteoporosis. Women generally have lower bone density as compare to their male peers and they lose bone mass quickly as they age. The International Osteoporosis Foundation estimates that osteoporosis affects about 200 million women worldwide. One of every two women over age 50 will likely have an osteoporosis related fracture in their lifetime. The good news is that this disease is highly preventable if bone health is maintained appropriately. And it is never too late to keep bones strong and avoid fracture.
RISK FACTORS
AGE: Bone mass begins to decline naturally with age and decreased bone density and strength increases the risk of osteoporosis.
GENDER: Women are 4 times more likely than men to develop it.
ETHNICITY: Research has shown that you are at greatest risk of osteoporosis if you are white or of asian descent.
FAMILY HISTORY: Heredity is one of the most important risk factor for osteoporosis.
SMOKING AND DRINKING: High intake of alcohol and tobacco leads to thinning of bones and increases the risk of fracture.
CERTAIN DISEASES: Some diseases like rheumatoid arthritis increases the risk of developing osteoporosis.
CERTAIN MEDICATION: Use of some medicines like long term use of steroids.
VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY: Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium. When Vitamin D is lacking, the body cannot absorb adequate amounts of calcium to prevent osteoporosis.
SEX HORMONES: Infrequent menstrual cycles and estrogen loss due to menopause may increase the risk.
SEDENTARY LIFESTYLE: Inadequate physical activity is also one of the leading factor.
BREAST CANCER
Breast Cancer is the most common invasive cancer in females worldwide.
It is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the breast. The damaged cells can invade surrounding tissue, but with early detection and treatment, most people continue a normal life. It can occur at any age but most commonly seen after the age of 40. Nobody knows the exact cause behind it. As per studies, it is caused by the damage to a cell’s DNA, but why and how that DNA gets damaged is still unknown.
ALSO READ: Fight Cancer Naturally With Anti-Cancer Foods
RISK FACTORS
Check out more about potential risk factors.
Don’t think you are immune to this problem, just because your mother didn’t have breast cancer. At the same time, it’s also important to note that some women who have one or more risk factors never get breast cancer.

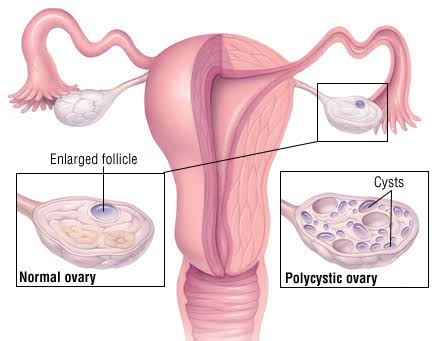
POLYCYSTIC OVARIAN SYNDROME (PCOS)
This condition leads to the growth of small cysts in the ovaries which are not harmful but causes imbalance in woman’s levels of the sex hormones ( estrogen and progesterone ).
It can cause problems with menstrual cycle and is one of the most common cause of infertility in woman. PCOS also leads to unwanted changes in the way you look ( acne, excess body and facial hair ). Early diagnosis and treatment can help control the symptoms and prevent long term problems.
ALSO READ: Control PCOS By Making 5 Lifestyle Changes
RISK FACTORS
Exact cause of PCOS is unknown, still HORMONAL IMBALANCES and GENETICS play a role.
FAMILY HISTORY : Women are more likely to develop PCOS if their mother or sister also has the condition. It can be passed down from either your mother’s or father’s side.
Family history of diabetes may increase your risk for PCOS.
CERTAIN MEDICATION : Long term use of seizure medicines has been linked to an increased risk of PCOS.
High insulin levels can increase production of androgens which interfere with ovulation and contribute to PCOS.
ANAEMIA
Decrease in the amount of healthy RBC or haemoglobin (Hb) in the blood leads to a condition called Anaemia. Hb is a main part of RBCs and are responsible for transporting oxygen throughout the body. In its shortage, cells in your body will not get enough oxygen. All this leads to a variety of symptoms like fatigue, pallor (pale skin colour), weakness, breathlessness, heart palpitation, hair loss etc.
There are different types of anaemia, IRON DEFICIENCY ANAEMIA is the most common type of anaemia. It occurs when you do not have enough iron in your body. For that you need to take proper diet rich in iron.
RISK FACTORS
AGE : People over the age of 65 are at increased risk of anaemia.
FAMILY HISTORY : If your family has a history of an inherited anaemia, like sickle cell anaemia or thalassemia, you are likely to suffer from it.
FEMALES : Women of childbearing age are at higher risk for developing this condition because of blood loss from menstruation.
Pregnant women who are not taking multivitamin with folic acid are at higher risk because they need twice as much iron as usual especially for growth of fetus.
INTESTINAL DISORDER : Having an intestinal disorder that affects the absorption of nutrients in your small intestine — such as Crohn’s disease and celiac disease — puts you at risk of anemia.
CHRONIC CONDITIONS : If you have cancer, kidney failure or another condition that cause chronic blood loss, you may be at risk of anemia of chronic disease. These conditions can lead to a shortage of red blood cells.
URINARY TRACT INFECTION (UTI)
UTI is the 2nd most common type of infection in the body. 40-50% of women have atleast one UTI during their lifetime with 20-30% experience recurrent UTI. Common symptoms include strong, frequent urge to urinate, painful and burning sensation when urinating, strong smelling urine with blood or pus in it. Some people experience abdominal pains and irritating pain during sexual intercourse.
A UTI is basically an infection of any part of urinary system. Most infections involve the lower urinary tract (comprised of the bladder, kidneys, ureters and urethra). These infections typically occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra and begin to multiply in the bladder. UTI is 10 times more common among women than men.
RISK FACTORS
Sexual intercourse (especially if more frequent, intense and with multiple or new partners)
Diabetes.
Poor personal hygiene.
Problems emptying the bladder completely.
Having a urinary catheter.
Bowel incontinence.
Kidney stones.
Pregnancy.
Menopause
Suppressed immune system.
Immobility for a long period.
Heavy use of antibiotics (which can disrupt the natural flora of the bowel and urinary tract).
Use of irritating products, such as harsh skin cleansers.
Use of irritating contraceptives, such as diaphragms and spermicides.
Use of birth control pills.
A blockage in the urinary tract (benign masses or tumors).
A history of UTIs, especially if infections are less than 6 months apart.

“TAKE CARE OF YOUR BODY,
IT’S THE ONLY PLACE YOU HAVE TO LIVE.”
